Hometown: Orange County, CA
Lab: Neal Devaraj Lab, UC San Diego
Lab website: https://www.devarajgroup.com/
Hobbies: Dancing, concerts, traveling
What do you study?
Cancer, specifically post-translational modifications (PTMs) on proteins mutated in cancer. About one-third of all human cancers have mutations in the Ras family of proteins, but there are currently no treatments. For my research, I have used small-molecule compounds to target a PTM, called palmitoylation, in order to prevent Ras function in cancer.
Why is it important?
By targeting palmitoylation, we can develop better treatments that remove chemical modifications from proteins that are mutated in cancer. This type of research applies basic chemical approaches to solve biomedical problems. These treatments could someday be used by a doctor to help a patient suffering from cancer.
What piqued your interest in science?
My high school science teachers really contributed to my interest in pursuing a science career. It is very important to have great teachers who are passionate about science, who are always there to help answer your questions, and who make science fun with hands-on learning.
What do you like about being a scientist?
The best part about being a scientist is being able to answer unsolved questions, knowing that my research is contributing to developing better treatments. I enjoy doing the hands-on experiments in the laboratory, constantly learning something new every day, and working with other scientists from a variety of scientific disciplines.
What are 5 general vocabulary terms someone should know going into your field of science?
Chemical biology, cancer, drug discovery, small-molecule inhibitors, oncogenes
What are 5 specific vocabulary terms someone should know about your research?
Post-translational modifications, palmitoylation, Ras proteins, signaling pathways, melanoma
Sneak peak:
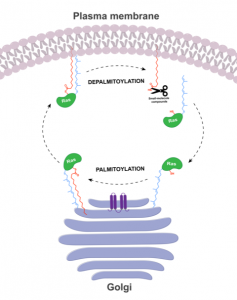
The picture below describes the cellular process of palmitoylation. Ras proteins are palmitoylated in the cell at the Golgi compartment and then are transferred to the plasma membrane. The small-molecule compounds that have been developed for depalmitoylation are able to directly cut off this chemical modification, which allows proteins to go back to the Golgi.